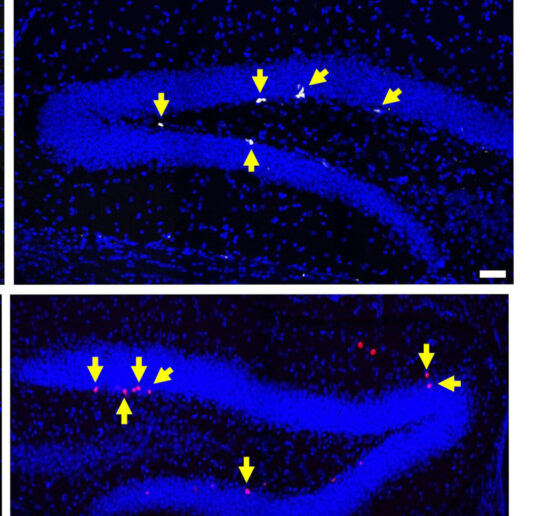
Studies by a growing number of labs have identified neurological health benefits from exposing human volunteers or animal models to light, sound and/or tactile stimulation at the brain’s “gamma” frequency rhythm of 40Hz. In the latest such research at The Picower Institute for Learning and Memory and Alana Down Syndrome Center at MIT, scientists found that 40Hz sensory stimulation improved cognition and circuit connectivity and encouraged the growth of new neurons in mice genetically engineered to model Down syndrome.
Li-Huei Tsai, Picower Professor at MIT and senior author of the new study in PLOS ONE, said that the results are encouraging but also cautioned that much more work is needed to test whether the method, called GENUS (for Gamma Entrainment Using Sensory Stimulation), could provide clinical benefits for people with Down syndrome.